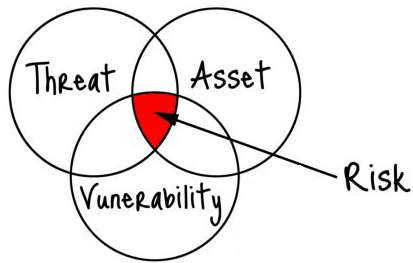
CIOs—Unsung Heroes
In my 35+ years of being a corporate change agent, and now at the helm of my own consultancy, I have worked with all levels of the C-suite, and I have to say the CIO role is by far the most difficult. There are numerous reasons for this, not the least of which is an outdated model of the C-suite itself.
The fact is that most companies still view IT and the CIO role through the narrow lens of providing technology-based services; they have not broadened that view to take into account the stunning changes wrought by digital technology. IT is no longer simply responsible for building, operating, and maintaining infrastructure; it’s responsible for data governance, driving growth through data analytics, cyber security, connectivity and integration. However, since most organizations are peering through the old lens of IT-as-service-provider, they are blind to IT as a revenue-producer. The irony here is that Sales, Marketing, R&D, Finance, and HR—those typically considered revenue-producing—are only able to do what they do because of IT and IT’s ability to stay ahead of the curve.
According to a recent IBM study of 4,100 C-suite executives, only 42% of CIOs were involved in strategy, as opposed to 72% for CFOs and 63% for CMOs. This is puzzling. Since IT touches everything, the CIO has an enterprise-wide vision that would be invaluable in integrating an enterprise-wide strategy. Luckily, the IBM study suggests that this is turning around—the CIO is soon going to be considered one of the C-suite “triumvirate,”: CEO, CIO, CMO.
Another reason the CIO role is more difficult than most is that it bears sole responsibility for ensuring business continuity through critical service level agreements that define uptime, availability and redundancy. …
[ Read More ]